Resources
Clinical resources for healthcare providers
Find clinical resources to support your gastroparesis patients and practice.
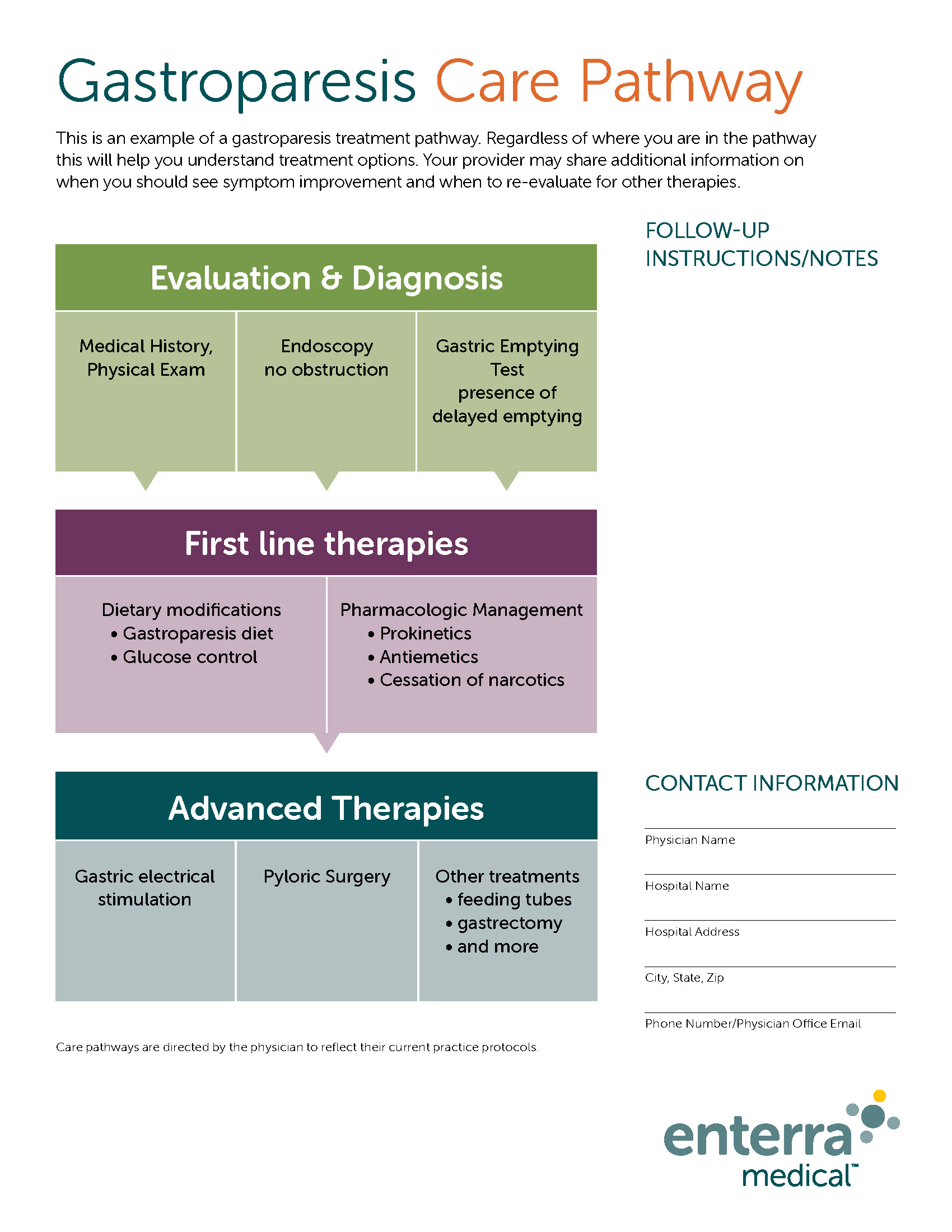
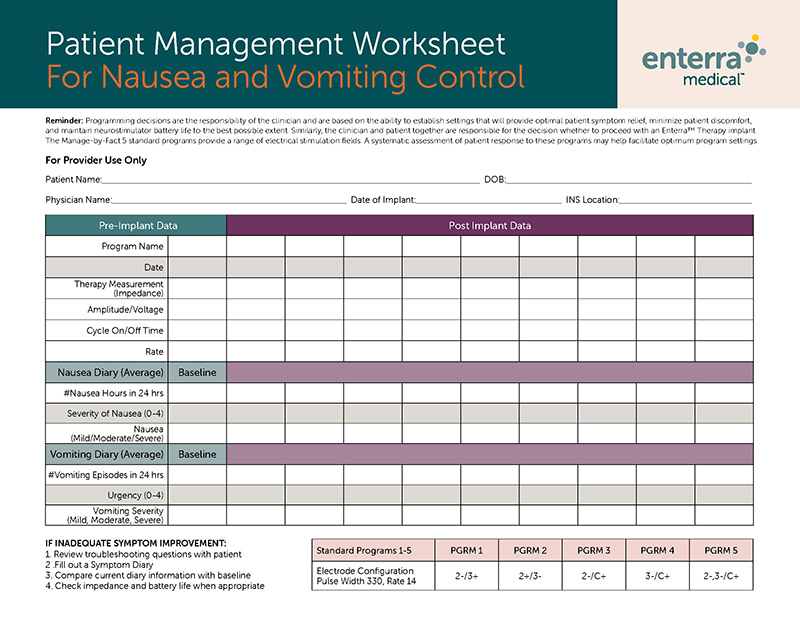
Screening and referral
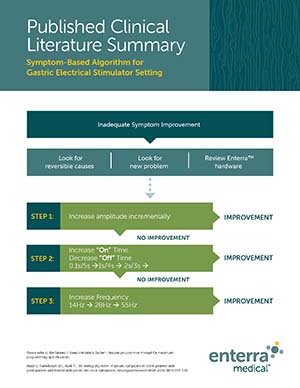
Practice guidelines
- Lacy BE, Tack J, Gyawali CP. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Management of Medically Refractory Gastroparesis: Expert Review [published online ahead of print, 2021 Oct 29]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;S1542 3565(21)01151 4. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2021.10.038.
- Camilleri, et al. ACG Clinical Guidelines: Gastroparesis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022 Aug 1;117(8):1197-1220. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000001874.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Enterra Therapy for treatment of chronic, resistant to medication nausea and vomiting associated with gastroparesis caused by diabetes or an unknown origin in patients aged 18 to 70 years: patients should always discuss potential risks and benefits of the device with their physician.
HUMANITARIAN DEVICE
Authorized by Federal law for use in the treatment of chronic intractable (drug refractory) nausea and vomiting secondary to gastroparesis of diabetic or idiopathic etiology in patients aged 18 to 70 years. The effectiveness of this device for this use has not been demonstrated. What does this mean?